Navigating Tax Benefits: A Comparative Analysis of Non-Habitual Residence (NHR) Tax Regime and IFICI+ Tax Benefit

Diogo Pedro | Tax Consultant
Since 2009, Portugal has been actively encouraging the arriving of new residents through the Non-Habitual Resident (NHR) regime. This initiative aims to attract both capital and expertise to our country by inviting individuals to establish residence in Portugal.
Under this regime, individuals who have not been residents in Portugal in the last 5 years, and whose incomes are subject to taxation in their home country, are granted a 10-year exemption from personal income tax (IRS).
Furthermore, the NHR regime offers the option to tax income from labour and freelance work at an autonomous tax rate of 20%, along with a 20% withholding tax rate for labour incomes. This specifically applies to activities characterised by a high level of scientific, artistic, or technical value.
However, the NHR regime has been revoked and now Portugal has introduced a new tax benefit to replace it.
This new tax incentive aims to promote high-value activities and is outlined in Article 58.º-A of the Tax Benefits Statute. The name of the regulated tax benefit is IFICI+.
This benefit includes:
- People lecturing in higher education and scientific research, along with participating in scientific roles within the national science and technology system. This includes employment opportunities within entities, structures, and networks, as well as positions and memberships in governing bodies within organizations recognized as technology and innovation centres.
- Skilled positions within the context of contractual benefits aimed at promoting productive investment, in alignment with Chapter II of the Portuguese Investment Tax Code.
- Individuals with jobs recognised by the Agency for Investment and Foreign Trade of Portugal, E.P.E., or by IAPMEI - Agency for Competitiveness and Innovation, I.P. as fundamental to the national economy (including those working in the Azores and Madeira, subject to conditions set by regional laws).
- Individuals engaged in research and development activities, whose expenses are eligible for the purposes of the tax incentive system in research and business development, as outlined in the Investment Tax Code.
- Individuals moving to Portugal to work for certified start-ups (companies with a staff of no more than 250 individuals, an annual income not exceeding 50 million euros and a business history of fewer than ten years), provided that the company’s headquarters are established in Portugal or have representation in the country. Alternatively, they must have at least 25 employees in Portugal. Moreover, these startups cannot result from a merger or division of a larger company.
- Job positions or other activities carried out by tax residents in the autonomous regions of the Azores and Madeira.
Now, let’s examine the practical differences between taxation under the NHR regime and the IFICI+ tax benefit.
For this purpose, we will consider an individual whose income results from a Portuguese salary, interest income, capital gains from real estate, capital gains from stocks and a private pension, all from white-listed countries.
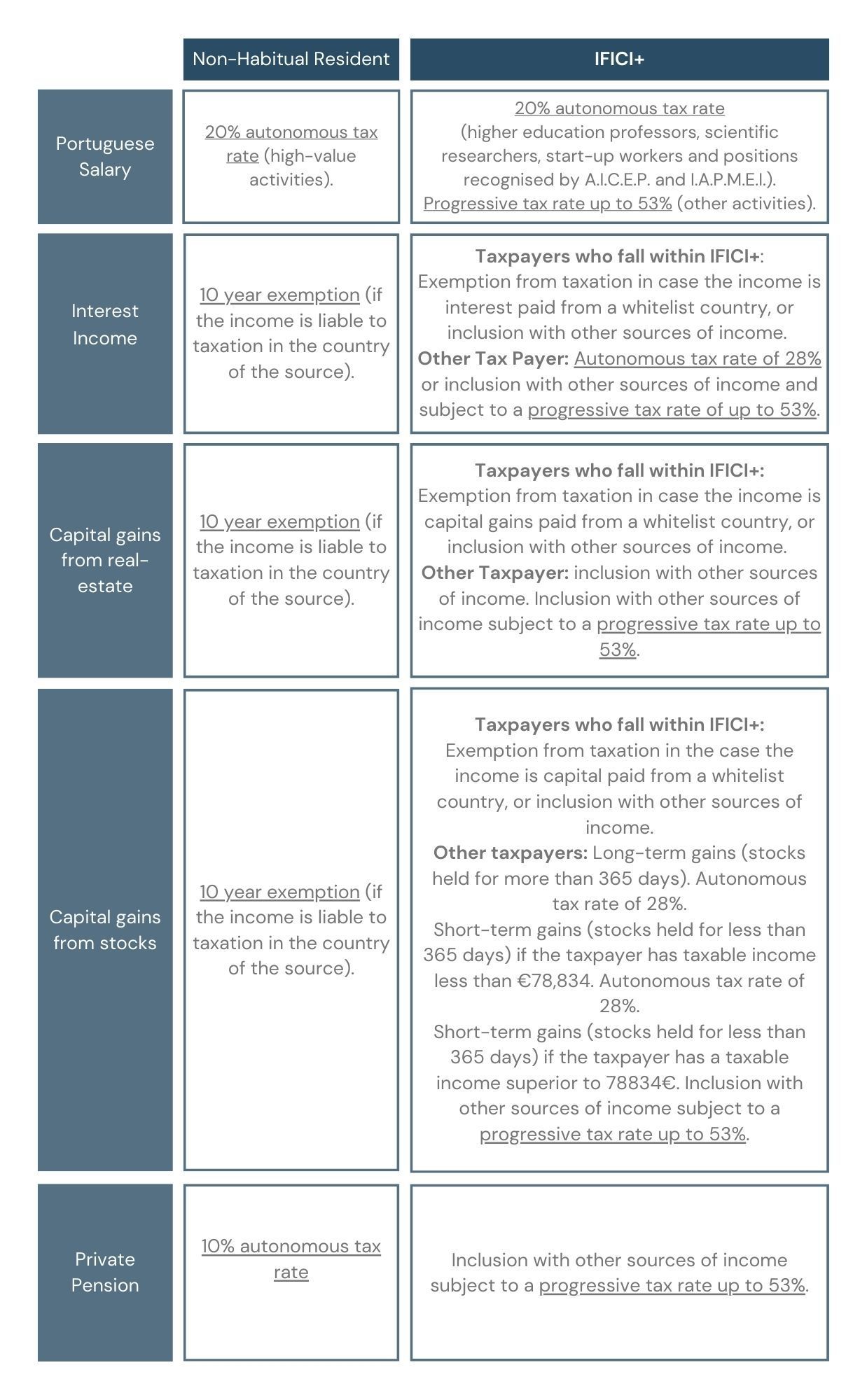
By analysing all this information, we can conclude that the IFICI+ tax benefit is notably more exclusive. It particularly focuses on education, R&D and entrepreneurship activities. However, taxpayers who fall within this new tax benefit can get an exemption from foreign income derived from white-listed countries.
This means that, even though the IFICI+ has a stricter range of applications, it can be more advantageous for the individuals who can benefit from it. Given the fact that there is no need for the income to be subjected to taxation or liable to taxation in the country of source, unlike the NHR regime.
With the IFICI+ tax benefit officially regulated through Regulation No. 352/2024/1 on the 23rd of December 2024, every foreign taxpayer in Portugal who fulfils the requirements can apply and benefit from this special regime.
If you have further questions regarding this matter or need help with the application, get in touch with us and we will be delighted to assist you.










