As a Portuguese Citizen, How Can I Pass the Citizenship To My Children?

Rafael Galhano de Almeida | Lawyer
The Portuguese law distinguishes between citizenship by origin and derivative citizenship.
The first one applies to the following situations:
- The children of Portuguese mothers or Portuguese fathers born in Portuguese territory;
- The children of Portuguese mothers or Portuguese fathers born abroad if the Portuguese parent is there in the service of the Portuguese State;
- The children of Portuguese mothers or Portuguese fathers born abroad if they have their birth registered in the Portuguese Civil Registry or if they declare that they want to be Portuguese;
- Individuals with at least one ascendant of Portuguese nationality of the 2nd degree in the straight line who has not lost that nationality, if they declare that they want to be Portuguese and have effective ties to the national community;
- Individuals born in Portuguese territory, children of foreigners, if at least one of the parents was also born here and has residence here, regardless of title, at the time of birth;
- Individuals born in Portuguese territory, children of foreigners who are not in the service of the respective State, who do not declare that they do not wish to be Portuguese, provided that, at the moment of birth, one of the parents legally resides in Portuguese territory, or has resided here, regardless of title, for at least one year;
- Individuals born in Portuguese territory and who do not hold any other nationality.
The second one includes all the other ways to acquire Portuguese citizenship, such as by living in Portugal for at least 5 years, by being married or in a civil partnership with a Portuguese citizen for at least 3 years, or by benefiting from the special regime for descendants of Sephardic Jews. To know more this text offered a detailed explanation of Portuguese Citizenship.
The citizenship by origin produces effects from birth. On the opposite side, derivative citizenship only produces effect since the date of its registration before the Portuguese Authority.
To be able to determine whether you can pass Portuguese citizenship to your children, it is crucial to consider the moment of your child’s birth and distinguish if the child, at the moment of submitting the application, is underage or already major [better explain in the table below].
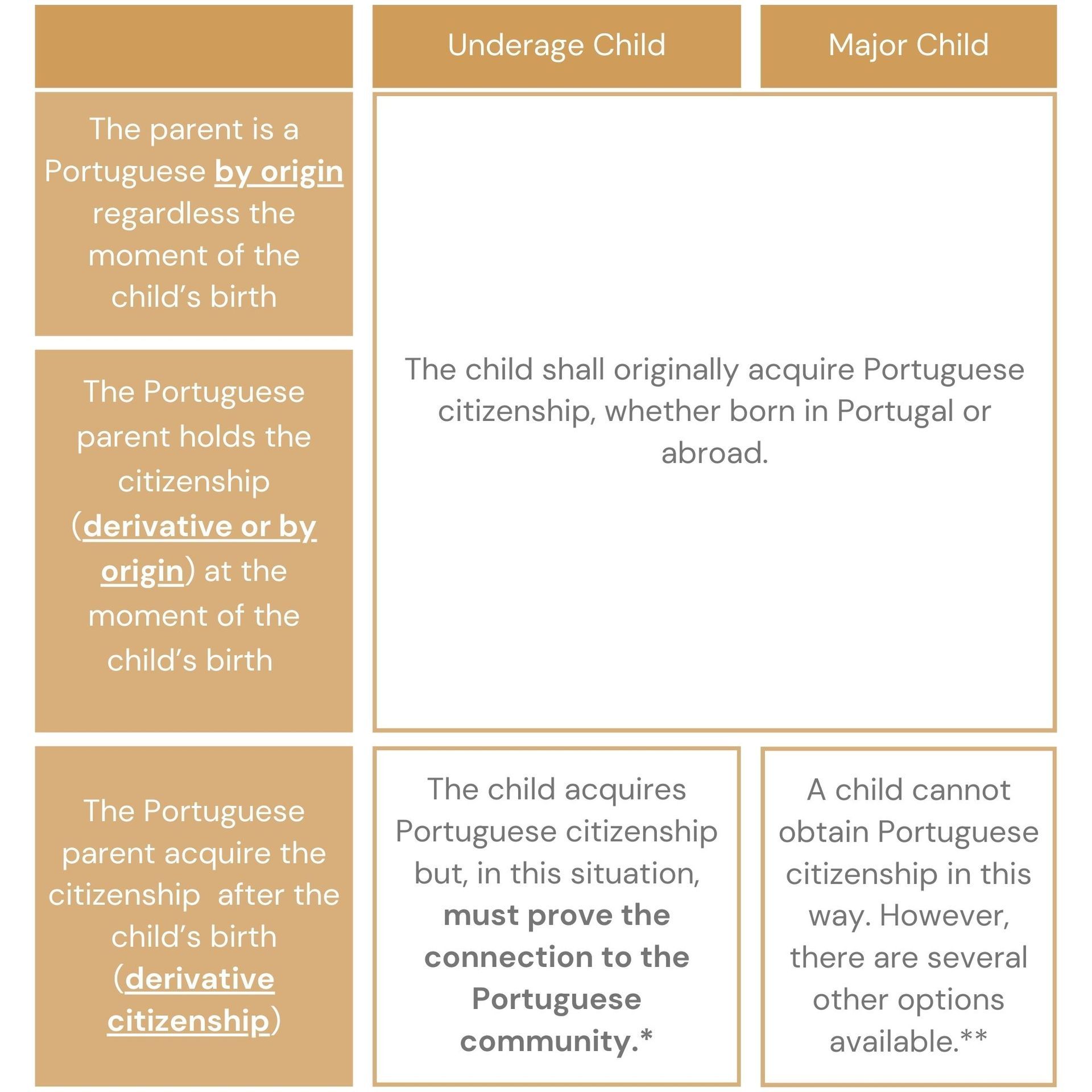
* For the case of children whose one of the parents acquired Portuguese citizenship after their birth, as explained in the table, it should be demonstrated the connection to the Portuguese community. There is a presumption of belonging to the Portuguese community with 5 years of residence in the Portuguese territory and proof of attending school in Portugal.
** If someone is born to a Portuguese parent who gained derivative Portuguese citizenship after their birth, and if this parent's citizenship was obtained through means other than descent, then the major child cannot acquire Portuguese citizenship through the parent. However, the child can still obtain citizenship through other means, such as residing in Portugal for a minimum of 5 years, being married or in a civil partnership with a Portuguese citizen for a minimum of 3 years, or by benefiting from the special regime for descendants of Sephardic Jews.
If the child is a minor or disabled, the Law states that the application should be submitted by the parents. If the child is a major (over 18 years old, according to Portuguese law), the application is made directly by him/her.
If you have further questions regarding this matter,
get in touch with us and we will be delighted to assist you.










